Essential Guide to Gastroparesis Diet Modification for Improved Digestion in 2025
Gastroparesis, a condition that affects the stomach’s ability to empty its contents, can significantly impact one's quality of life. A carefully tailored gastroparesis diet plays a crucial role in managing symptoms and improving overall digestive health. By modifying what you eat, you can alleviate discomfort and ensure better nutrition. In this article, we will explore effective dietary strategies, foods to incorporate, and lifestyle changes that can support those living with gastroparesis.
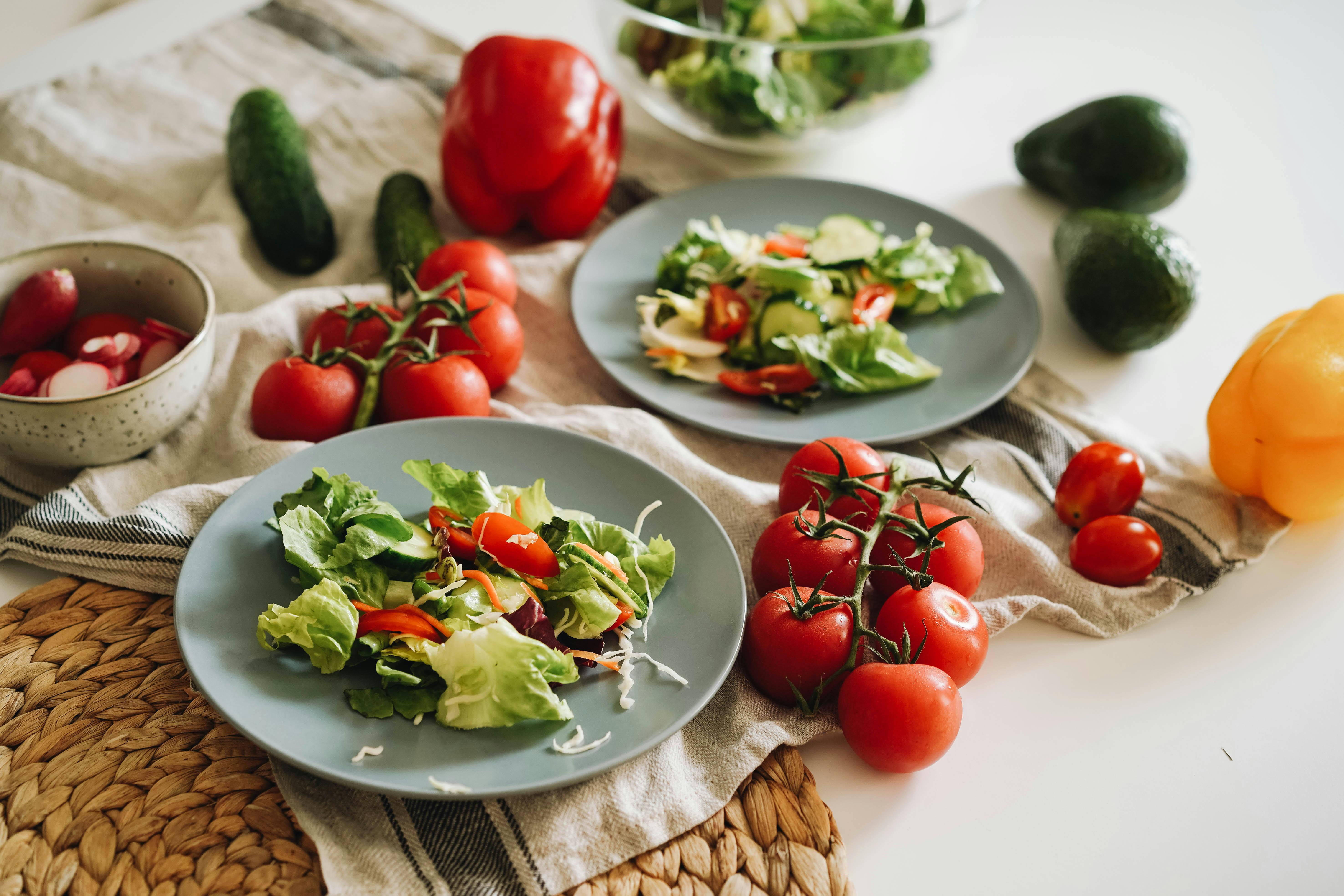

The benefits of a well-planned diet for gastroparesis extend beyond just reducing symptoms like nausea and bloating. Specifically designed meal plans can enhance nutrient absorption and provide a source of comfort amidst the challenges of the condition. We will cover a comprehensive gastroparesis meal plan, highlight foods to eat with gastroparesis, and identify what to avoid. Let's embark on this journey towards understanding how dietary adjustments can lead to improved digestive health.
In the following sections, we will discuss:
- The fundamentals of a gastroparesis-friendly diet
- Meal planning tips and recipe ideas
- Hydration and nutrition essentials
- Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
- Emotional aspects and support resources
Understanding Gastroparesis and Its Dietary Impact
Before diving into specific diets and meal plans, it is essential to understand what gastroparesis entails. This condition slows down the movement of food from the stomach to the small intestine, leading to various gastrointestinal issues. Many patients experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and early satiety, making it crucial to adjust dietary habits.
Overview of Gastroparesis Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of gastroparesis is the first step toward effective management. Common signs include:
- Nausea: Persistent feelings of queasiness can hinder food intake.
- Vomiting: In severe cases, undigested food may be expelled.
- Feeling full quickly: Many individuals find that small meals leave them feeling overly full.
By modifying your diet, these symptoms can be managed more effectively. Focusing on low-fiber, soft foods can enhance digestion, reducing discomfort significantly.
Importance of a Customized Meal Plan
Each individual’s experience with gastroparesis can differ greatly, which is why individualized meal planning is vital. Collaborating with a nutritionist can help to create a personalized nutritional assessment that considers both dietary restrictions and food preferences. This tailored approach can lead to better symptom management and overall well-being.
Breaking Down Dietary Goals
Setting realistic dietary goals is crucial. The primary targets include:
- Increasing nutrient-dense foods to avoid deficiencies
- Maintaining hydration to aid in digestion
- Incorporating small, frequent meals to manage fullness
Identifying suitable foods aligns with these goals, supporting a more comfortable eating experience.
Essential Foods to Include in a Gastroparesis Diet
After understanding the basis of gastroparesis and its dietary impact, let’s delve into the essential foods that should be incorporated into your diet.
Soft Foods: A Fundamental Component
Foods that are easy to digest and soft in texture are typically recommended for individuals with gastroparesis. Examples include:
- Mashed potatoes and applesauce
- Scrambled eggs and yogurt
- Creamy soups and smoothies
These items not only reduce the workload on the digestive system but also ensure that nutrient intake remains high even with limited food types.
Low Fiber and Low Fat Options
A low fiber diet is often advised as high-fiber foods can slow down digestion further. Favorable low-fat options can include:
- Non-fat dairy products
- Lean meats like chicken and fish
- Well-cooked vegetables
These foods help in facilitating smoother digestion while providing essential nutrients for energy and recovery.
Hydration Tips for Gastroparesis
Remaining hydrated is arguably one of the most important aspects of managing gastroparesis. Drinking fluids can aid digestion, especially when consuming solid foods. Opt for clear broths, herbal teas, and electrolyte drinks. Additionally, smoothies can serve as both hydration and nutrition sources when blended with soft foods.
Making hydration a priority not only promotes digestive health but also ensures well-being since dehydration can exacerbate symptoms.
Meal Planning and Preparation Strategies
With the right foods identified, let’s explore effective meal planning and preparation strategies that are vital for managing gastroparesis.
Creating Balanced Meals
A well-balanced meal for gastroparesis should include sources of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats in manageable portions. Consider incorporating:
- Low-fat dairy, such as cottage cheese, as a protein source
- White rice or pasta for carbohydrates
- Pureed or mashed fruits and vegetables for vitamins and minerals
Dividing meals into small portions can also ease digestive strain, allowing you to enjoy multiple smaller meals throughout the day instead of a few larger ones.
Cooking Methods That Benefit Digestion
Utilizing gentle cooking methods can enhance the digestibility of meals. Recommended techniques include steaming, boiling, or baking. Avoid frying or grilling as they can add unnecessary fat and complexity, aggravating your symptoms.
Meal Prep Tips for Time Management
Reducing meal preparation time can also alleviate stress associated with cooking. Prepare meals in batches, freeze portioned sizes, and utilize simple recipes that focus on easily digestible ingredients. For example:
- Batch-make soups and freeze portions
- Prepare smoothies in advance, freezing liquid portions for quick blending later
- Cook grains like rice or quinoa in larger quantities to use throughout the week
Efficient meal prep can preserve energy levels while ensuring consistent access to gastroparesis-friendly foods.
Tips for Eating Comfortably
Comfort is key in enhancing the dining experience for those with gastroparesis. Several eating tips can create a positive environment and encourage better digestion.
Setting Up an Enjoyable Eating Environment
Your dining setup can dramatically affect your meal experience. Aim for a comfortable, quiet setting to minimize distractions. Consider using adaptive dining tools, like ergonomic utensils that make it easier to eat and enjoy food.
Mindful Eating Practices
Taking your time during meals can aid digestion significantly. Focus on each bite, ensuring it is chewed well in order to ease the digestive burden. Mindful eating also means acknowledging your body's signals and eating slowly to prevent feeling overwhelmed.
Incorporating Family and Community in Meals
Involving family in meals can provide emotional support and reduce feelings of isolation often associated with dietary restrictions. Planning meals together can not only provide encouragement but also lead to discovering new gastroparesis-friendly recipes.
Closing Remarks: Resources and Support
Living with gastroparesis can be challenging, but numerous resources are available to assist. Engaging with support groups, using meal planning assistance programs, and working closely with dietitians can enhance your management strategies significantly.
Understanding the emotional implications of dietary changes is also crucial. Finding communities or online forums where others share experiences can foster a supportive atmosphere. Check out patient resources for more information and valuable insights.
In the journey of managing gastroparesis, the right dietary modifications can lead to a new level of comfort and improved digestive health. By taking small steps toward adjusting your diet, you can effectively manage your symptoms and enhance your quality of life.